NMN Octa 3000
RichwayThis Product Is Discontinued
NMN Octa 3000™ supplement that creates energy and helps with age-related health issues. It contains the world’s best NMN, Uthever NMN, with enhanced absorption. Ingredients include:
- NMN Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
- Pterostilbene
- L-Arginine
- Octacosanol
- Soy isoflavone
- Maca
USA Shipping only.
Richway NMN Octa 3000TM Supplement Facts
▶ Serving Size : 2 Capsules
▶ Servings Per Container : 30
Amount Per Serving
NMN Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: 250 mg
Pterostilbene: 25 mg
L-Arginine: 250 mg
Octacosanol: 187 mg
Soy Isoflavone: 70 mg
Daily Value not established
Richway NMN Octa 3000TM Ingredients
- NMN Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
- L-Arginine
- Octacosanol
- Pterostilbene
- Soy Isoflavone
- Silk peptide
- Maca Concentrate Powder
- Zinc Oxide
- Silicon Dioxide
- Vitamin A Mixture
- Vitamin D3 Mixture
- Calcium Pantothenate
- Vitamin B1 hydrochloride
- Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B6 hydrochloride
- Nicotinic acid amide
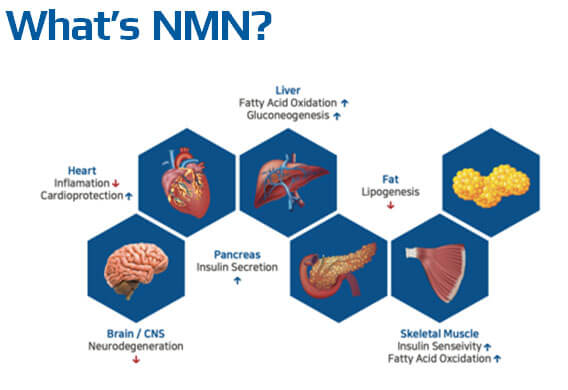
What’s NMN?
NMN stands for nicotinamide mononucleotide, a molecule naturally occurring in all life forms. At the molecular level, it is a ribo-nucleotide, which is a basic structural unit of the nucleic acid RNA. Structurally, the molecule is composed of a nicotinamide group, a ribose and a phosphate group. NMN is the direct precursor of the essential molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and is considered a key component to increasing NAD+ levels in cells.
What is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)?
NAD+ is an essential coenzyme required for life and cellular functions. Enzymes are catalysts that make biochemical reactions possible. Coenzymes are ‘helper’ molecules that enzymes need in order to function.
What Does NAD+ Do?
NAD+ is the most abundant molecule in the body besides water, and without it, an organism would die. NAD+ is used by many proteins throughout the body, such as the sirtuins, which repair damaged DNA. It is also important for mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of the cell and generate the chemical energy that our bodies use.
NAD+ Functions as a Coenzyme in Mitochondria
NAD+ plays an especially active role in metabolic processes, such as glycolysis, the TCA Cycle (AKA Krebs Cycle or Citric Acid cycle), and the electron transport chain, which occurs in our mitochondria and is how we obtain cellular energy. In its role as a ligand, NAD+ binds to enzymes and transfers electrons between molecules. Electrons are the atomic basis for cellular energy and by transferring them from one molecule to the next, NAD+ acts through a cellular mechanism similar to recharging a battery. A battery is depleted when electrons are expended to provide energy. Those electrons can’t return to their starting point without a boost. In cells, NAD+ serves as that booster. In this way, NAD+ can decrease or increase enzyme activity, gene expression, and cell signaling.
NAD+ Might Help Control DNA Damage
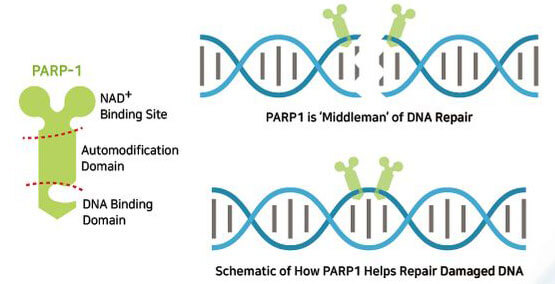
As organisms grow older, they accrue DNA damage due to environmental factors such as radiation, pollution, and imprecise DNA replication. According to the current aging theory, the accumulation of DNA damage is the main cause of aging. Almost all cells contain the ‘molecular machinery’ to repair this damage. This machinery consumes NAD+ and energy molecules. Therefore, excessive DNA damage can drain valuable cellular resources.
One important DNA repair protein, PARP (Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase), depends on NAD+ to function. Older individuals experience decreased levels of NAD+. The accumulation of DNA damage as a result of the normal aging process leads to increased PARP, which causes decreased NAD+ concentration. This depletion is exacerbated by any further DNA damage in the mitochondria.
NAD+ is the fuel that helps sirtuins sustain genome integrity and promote DNA repair. Like a car cannot drive without fuel, sirtuins’ activation requires NAD+. Results from animal studies showed that raising NAD+ levels in the body activates sirtuins and increases the lifespans of yeast, worms, and mice.
Although animal studies showed promising results in anti-aging properties, scientists are still studying how these results can translate to humans. NAD+ is one of the keys to maintaining healthy mitochondrial functions and steady energy output. Aging and a high-fat diet reduce the level of NAD+ in the body. Studies have shown that taking NAD+ boosters can alleviate diet-associated and age-associated weight gain in mice and improve their exercise capacity, even in aged mice. Other studies even reversed the diabetes effect in female mice, showing new strategies to fight metabolic disorders, such as obesity.
How is NMN Synthesized In the Body?
NMN ATP NAD+ NMN is produced from B vitamins in the body. The enzyme responsible for making NMN in the body is called nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT). NAMPT attaches nicotinamide (a vitamin B3) to a sugar phosphate called PRPP (5’-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate). NMN can also be made from ‘nicotinamide riboside’ (NR) through the addition of a phosphate group. ‘NAMPT’ is the rate-limiting enzyme in the production of NAD+. This means lower levels of NAMPT cause decreased NMN production, resulting in decreased NAD+ levels. Adding precursor molecules like NMN can also speed up NAD+ production.

How to Increase NAD+ levels
Fasting or reducing calorie intake, better known as calorie restriction, has been shown to increase NAD+ levels and sirtuin activity. In mice, the increased NAD+ and sirtuin activity from calorie restriction has been shown to slow the aging process. Although NAD+ is present in some foods, the concentrations are too low to affect intracellular concentrations. Taking certain supplements, such as NMN, has been shown to increase NAD+ levels.
NAD+ Supplement as NMN
Intracellular concentrations of NAD+ decrease from aging as normal cellular functions deplete NAD+ supplies over time. Healthy levels of NAD+ are thought to be restored by supplementation with NAD+ precursors. According to research, precursors such as NMN and nicotinamide riboside (NR) are viewed as supplements of NAD+ production, increasing concentrations of NAD+. David Sinclair, a NAD+ researcher from Harvard, says, “Feeding or administering NAD+ directly to organisms is not a practical option. The NAD+ molecule cannot readily cross cell membranes to enter cells, and therefore would be unavailable to positively affect metabolism. Instead, precursor molecules to NAD+ must be used to increase bioavailable levels of NAD+.” This means NAD+ cannot be used as a direct supplement because it is not easily absorbed. NAD+ precursors are more easily absorbed than NAD+ and are more effective supplements.
The History of the Biochemistry of NAD+
The coenzyme NAD+ was first discovered by the British biochemists Arthur Harden and William John Young in 1906. They noticed that adding boiled and filtered yeast extract greatly accelerated alcoholic fermentation in unboiled yeast extracts. They called the unidentified factor responsible for this effect a coferment. Through a long and difficult purification from yeast extracts, this heat-stable factor was identified as a nucleotide sugar phosphate by Hans von Euler-Chelpin. In 1936, the German scientist Otto Heinrich Warburg showed the function of the nucleotide coenzyme in hydride transfer and identified the nicotinamide portion as the site of redox reactions. Arthur Harden co-discoverer of NAD Vitamin precursors of NAD+ were first identified in 1938, when Conrad Elvehjem showed that liver has an "anti-black tongue" activity in the form of nicotinamide. Then, in 1939, he provided the first strong evidence that niacin is used to synthesize NAD+. In the early 1940s, Arthur Kornberg was the first to detect an enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway. In 1949, the American biochemists Morris Friedkin and Albert L. Lehninger proved that NADH linked metabolic pathways such as the citric acid cycle with the synthesis of ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. In 1958, Jack Preiss and Philip Handler discovered the intermediates and enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of NAD+; salvage synthesis from nicotinic acid is termed the Preiss-Handler pathway. In 2004, Charles Brenner and co-workers uncovered the nicotinamide riboside kinase pathway to NAD+.
Physical and chemical properties of NAD+
The compound accepts or donates the equivalent of H-. Such reactions (summarized in formula below) involve the removal of two hydrogen atoms from the reactant (R), in the form of a hydride ion (H-), and a proton (H+). The proton is released into solution, while the reductant RH2 is oxidized and NAD+ reduced to NADH by transfer of the hydride to the nicotinamide ring.
RH2 + NAD+ → NADH + H+ + R;
From the hydride electron pair, one electron is transferred to the positively charged nitrogen of the nicotinamide ring of NAD+, and the second hydrogen atom transferred to the C4 carbon atom opposite this nitrogen. The midpoint potential of the NAD+/NADH redox pair is 0.32 volts, which makes NADH a strong reducing agent. The reaction is easily reversible, when NADH reduces another molecule and is re-oxidized to NAD+. This means the coenzyme can continuously cycle between the NAD+ and NADH forms without being consumed.

NMN Octa 3000 In-Depth Ingredient Information
Pterostilbene
A close relative of resveratrol, Pterostilbene stands as a mighty warrior in the battle against aging. Supporting heart health and blood flow, it mimics calorie restriction, which is a known way to prolong lifespan. Its potential to enhance cellular energy and to act as an essential coenzyme to maintain healthy levels in cells is unparallel. Pterostilbene is a key to unlocking a world where your cells stay young, vibrant, and full of life.
It is a naturally occurring polyphenol, primarily found in blueberries, that has grabbed the attention of health enthusiasts and scientists alike. Pterostilbene is believed to support various aspects of health, including heart and cellular health, through its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Research suggests that Pterostilbene may help improve heart health by supporting cholesterol and blood pressure levels that are already within the normal range. Additionally, its impact on cellular health is noteworthy; it helps promote the integrity of the cell membrane, thus enhancing cellular function and longevity.
Pterostilbene is also associated with benefits on cognitive function and brain health, possibly aiding in the maintenance of memory and cognitive abilities as one ages.
With parallels to resveratrol, Pterostilbene offers enhanced bioavailability, meaning the body can use it more efficiently, potentially leading to more significant health outcomes.
While its full potential is still being unraveled, Pterostilbene's promising qualities make it an intriguing supplement for those pursuing a healthier life.
Octacosanol
Found in the tough layers of plant wax, Octacosanol is a unique alcohol that propels the cellular engine. It's known to boost stamina and improve blood vessel health – benefits every heart is yearning for. Think of Octacosanol as the oil in your body's machinery, ensuring that every part runs smoothly and efficiently, providing the best environment for cellular health.
Octacosanol, a straight-chain aliphatic 28-carbon primary fatty alcohol, is gaining considerable attention for its potential health benefits. Found naturally in several vegetable oils, wheat germ being one of the richest sources, and in smaller amounts in whole grains, octacosanol is primarily recognized for its role in maintaining heart health and improving physical performance.
Health Benefits of Octacosanol:
- Heart Health: Octacosanol may help reduce cholesterol levels, thus promoting better heart function.
- Endurance: Its intake is associated with increased stamina and energy, making it a favorite among athletes.
- Muscle Function: It may aid muscle strength and reduce cramping, contributing to overall muscular health.
- Nervous System Health: Octacosanol supports the normal function of the nervous system.
This compound's therapeutic properties have been explored in various studies, hinting at a role in mitigating oxidative stress and regulating lipid metabolism, which further underscores its potential in supporting cardiovascular health. As octacosanol continues to be explored, its inclusion in diet and supplementation might represent a proactive measure for individuals seeking to improve their overall well-being.
Isoflavones
Isoflavones, often associated with soy products, are a class of phytochemicals recognized for their remarkable health benefits. As potent antioxidants, they play a critical role in protecting cells against oxidative damage. Structurally similar to estrogen, they can bind to estrogen receptors, thereby exerting mild estrogenic effects which may alleviate menopausal symptoms and support bone health.
Research suggests that the inclusion of isoflavones in the diet may contribute to heart health by improving blood vessel elasticity and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. Moreover, they've been linked to a decreased risk for certain hormone-related cancers due to their ability to influence cell growth and apoptosis.
Isoflavones are also important for cellular energy as they can influence the pathways involved in cellular functions. By modulating signaling pathways, isoflavones aid in maintaining cellular health and longevity, thus showcasing their potential in anti-aging research.
For individuals seeking the benefits of isoflavones, they are abundantly found in legumes, particularly soybeans. Incorporating isoflavone-rich foods into the diet not only supports overall well-being but may also contribute to a healthier life at the cellular level.
Key Sources of Isoflavones:
- Soybeans and soy products
- Legumes
- Red clover
- Kudzu
Consider isoflavones as an essential part of your diet for their unique advantages in promoting long-term health and vitality.
Silk Peptide
Silk peptides, derived from the natural protein found in silk produced by the silk moth, have emerged as a potent ingredient gaining popularity in various health and beauty products. These small chains of amino acids are extracted through the careful hydrolysis of silk proteins, known as sericins and fibroins. What makes silk peptides so acclaimed is their ability to easily penetrate the skin and hair, due to their low molecular weight, providing a plethora of benefits that enhance beauty and well-being.
Benefits of Silk Peptides:
- Skin Hydration: Silk peptides aid in retaining moisture on the skin, leading to improved elasticity and a youthful complexion.
- Hair Strength: They bond with proteins in the hair, restoring its luster and protecting it from damage.
- Antioxidant Properties: Their antioxidant properties help in combating harmful free radicals.
- Collagen Production: They promote the production of collagen, essential for maintaining skin structure.
Applications of Silk Peptides:
- Skincare products (creams, serums)
- Haircare formulations (shampoos, conditioners)
- Nutritional supplements
Key Point: Silk peptides are an innovative and natural ingredient that can significantly enhance the health and appearance of skin and hair.
Maca
Maca, scientifically known as Lepidium meyenii, is a cruciferous vegetable native to the Andes of Peru. It's often referred to as Peruvian ginseng and is hailed for its various health benefits. Classically, maca root has been praised for its potential to enhance fertility and sex drive.
Maca is rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Notably, it contains Vitamin B1 hydrochloride, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B6 hydrochloride, which help in maintaining optimum health. These vitamins are essential for converting food into chemical energy and maintaining proper cellular functions.
The plant is also believed to have positive effects on hormonal balance, which can have cascading benefits for overall health, including potentially improved mood and energy levels. Furthermore, maca root includes beneficial bioactive compounds that could promote cellular health.
Studies have indicated that incorporating maca into the diet may contribute to increased endurance and mental clarity. However, while research is ongoing, the depth of maca's influence on cellular life and healthier living is still being decoded by science.
Here's a quick rundown of maca's impressive profile:
- Origin: Andes of Peru
- Also Known As: Peruvian ginseng
- Key Nutrients: Vitamin B1, B2, B6
- Health Claims: Increases fertility and sex drive, enhances mood, boosts endurance
- Research: Evidence of health benefits; ongoing studies into its full potential
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a critical nutrient for maintaining good health. It plays a pivotal role in calcium absorption, contributing to strong bones and teeth and supporting musculoskeletal health. Our bodies naturally produce Vitamin D3 when exposed to sunlight, but due to indoor lifestyles and certain latitudes, supplementation may be necessary.
This essential vitamin is also involved in modulating cell growth, immune function, and reducing inflammation. Adequate Vitamin D3 levels are important for heart health, and research suggests a correlation between higher levels of Vitamin D3 and a lesser risk of certain chronic illnesses.
Here's a quick overview of Vitamin D3:
| Function | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Bone Strength | Enhances calcium and phosphorus absorption |
| Immune System Support | Modulates the immune response |
| Anti-inflammatory | Reduces inflammation |
| Muscle Function | Improves muscle strength |
| Cardiovascular Health | Benefits heart and blood vessels |
It is important to maintain appropriate levels of Vitamin D3, which can be achieved through safe sun exposure, diet, and supplementation when necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplement to your regimen.
L-Arginine
L-Arginine, an essential amino acid, plays a pivotal role in various cellular functions. It serves as the substrate for the synthesis of nitric oxide, a molecule crucial for blood vessel health. This amino acid supports blood flow, promoting heart health and the delivery of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
L-Arginine also contributes to the synthesis of creatine, which assists in the production of cellular energy, fuelling various body processes. By fostering a healthy cell membrane, L-Arginine aids in blocking the paths that may lead to the malfunctioning of cells such as apoptosis in cancer cells, potentially inhibiting the growth and spread of cancer.
Recognized for its role in anti-aging research, L-Arginine, like Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN), appears to promote a healthier life at the cellular level. Arginine's transformation into essential molecules, such as Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+), underlines the importance of this amino acid in maintaining abundant energy levels in cells.
In short:
- Essential for heart health and blood flow
- Enhances cellular energy and health
- May contribute to cancer cell control
- Supports a healthier life at the cellular level
L-Arginine remains a cornerstone in the pursuit of optimum health, providing a foundation for researchers to build upon in the quest for longevity and vitality.






